My article, “Street Network Models and Indicators for Every Urban Area in the World” has been published by Geographical Analysis. This project was a massive undertaking and I’m excited to share it. As you might guess from the title, I modeled and analyzed the street network of each urban area in the world then deposited all the source code and models and indicators in open repositories for public reuse. The article also includes a high-level analysis of urban street network form across the world.
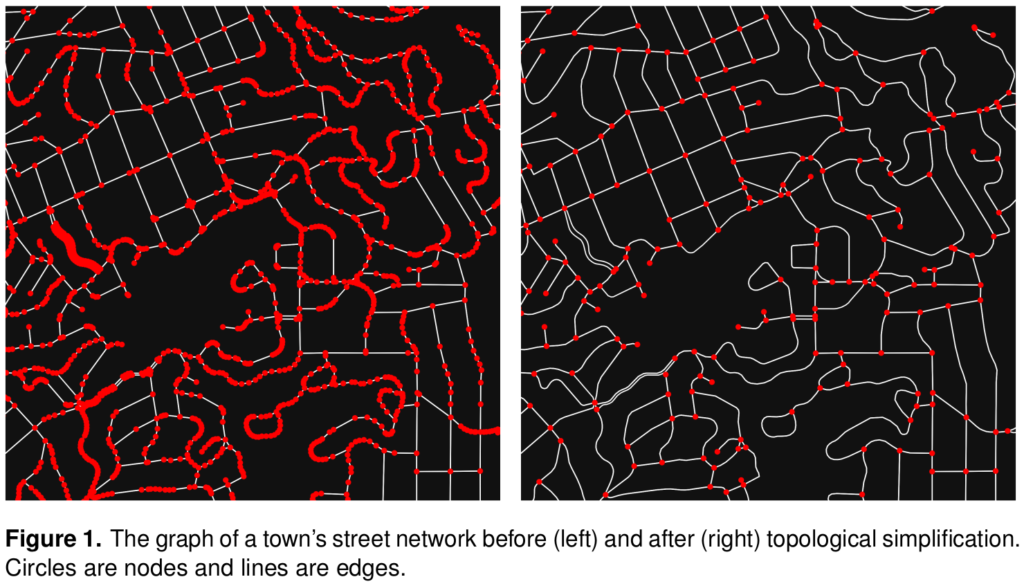
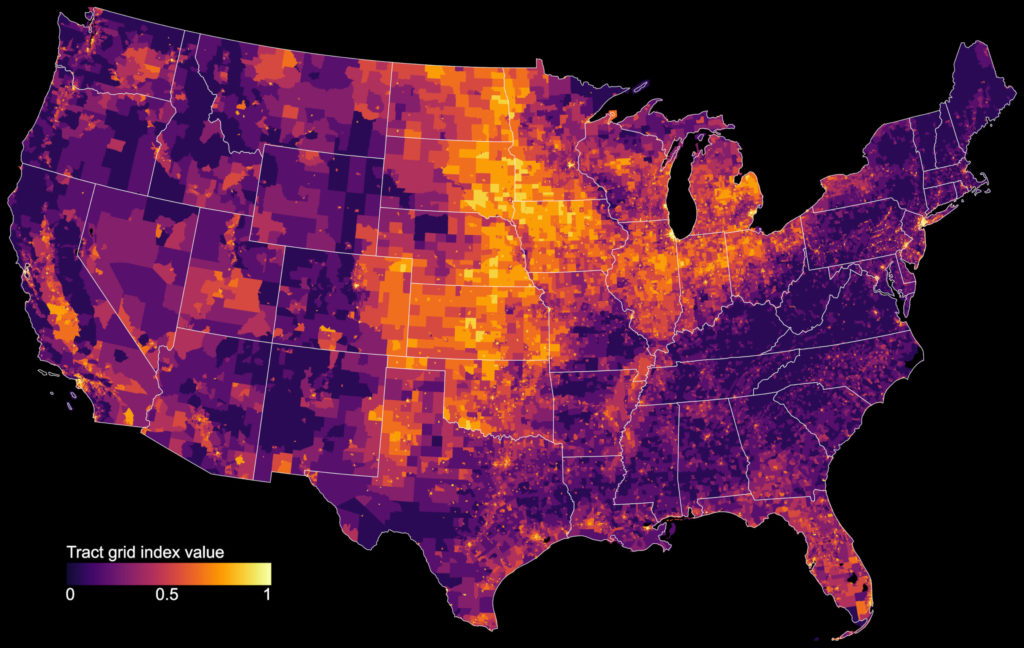
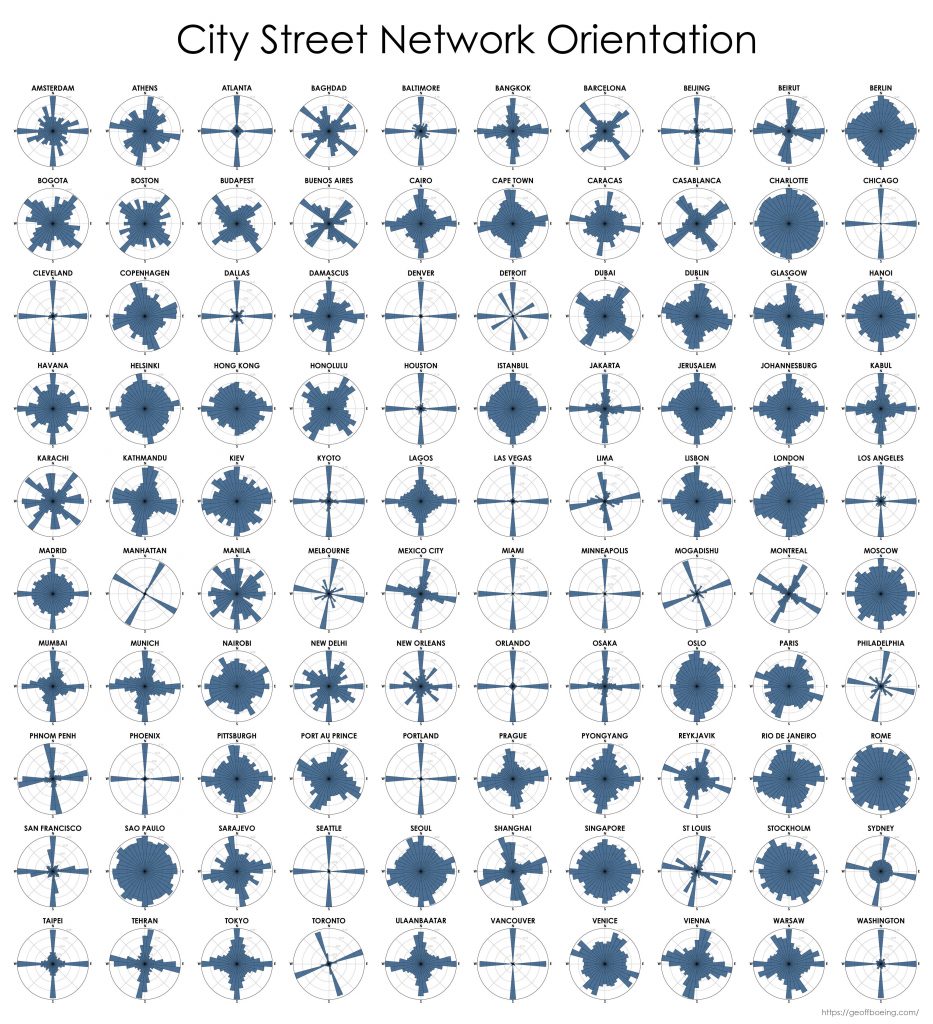
Cities worldwide exhibit a variety of street patterns and configurations that shape human mobility, equity, health, and livelihoods. Using boundaries derived from the Global Human Settlement Layer, I modeled and analyzed the street networks of every urban area in the world using OSMnx and OpenStreetMap raw data. In total, I modeled over 160 million street network nodes and over 320 million edges across 8,914 urban areas in 178 countries. I attached node elevations and street grades to every node/edge in the final models. All the final models were topologically simplified such that nodes represent intersections and dead-ends, and edges represent the street segments linking them.