Alongside Billie Giles-Corti and Jim Sallis, I will be presenting our team’s recent research into accessible, sustainable urban design around the world at the ISPAH Congress in Abu Dhabi this week. Our symposium at the congress will share the methods and findings from our The Lancet Global Health series published this summer, as well as our ongoing work on the Thousand Cities Challenge.
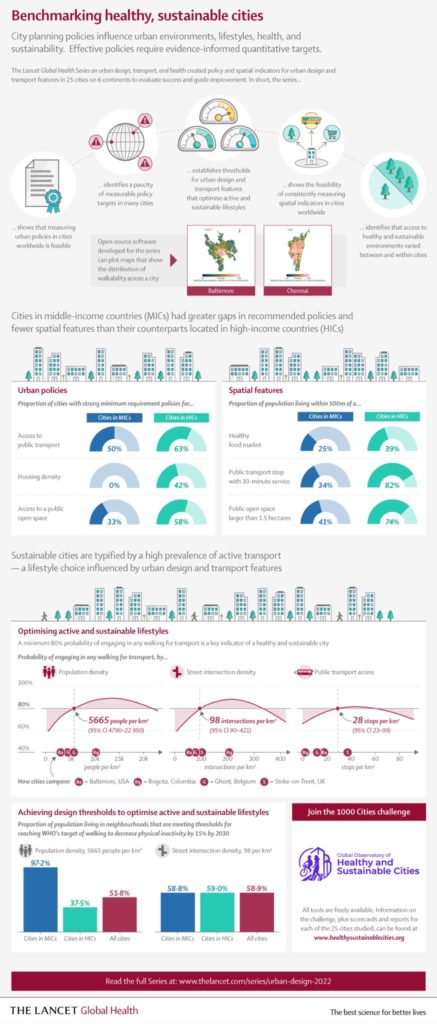
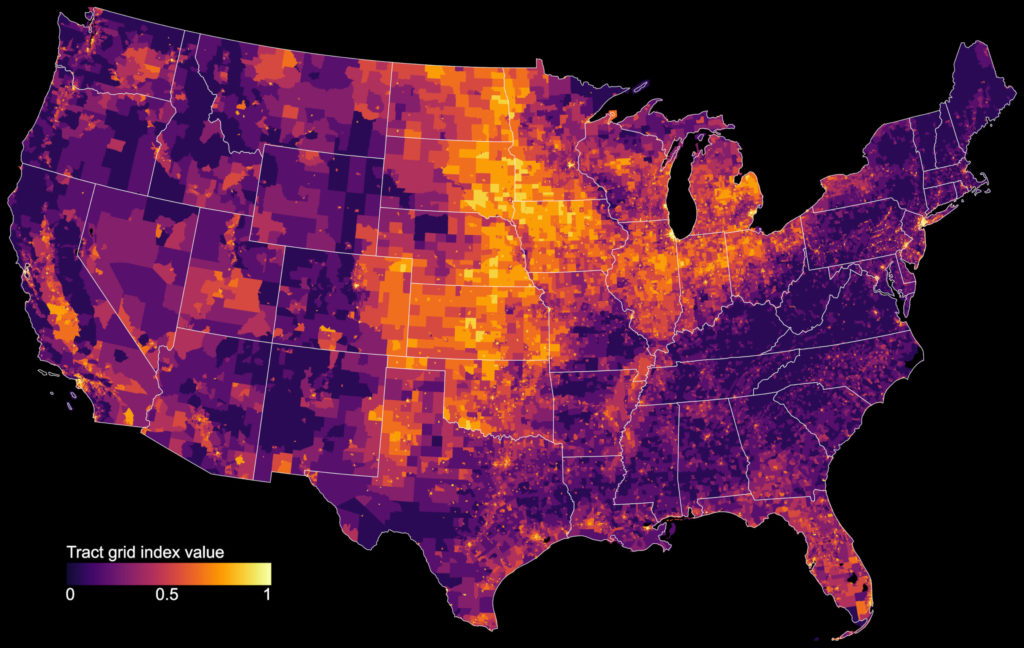
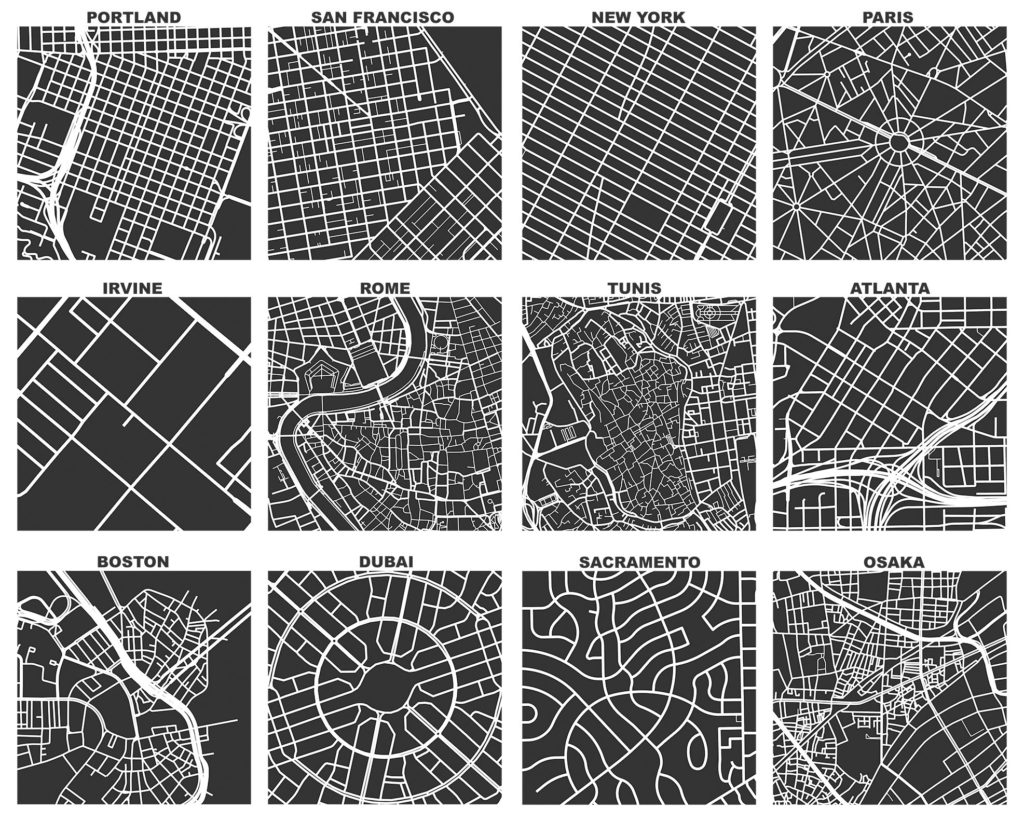
Our geospatial team developed open-source software to calculate indicators of walkability and accessibility around the world, and then linked these back to cities’ policy contexts and identified populations living above and below estimated thresholds for physical activity. Few cities had measurable policy standards and targets to actually build healthier and more sustainable cities, and their health-supportive built environment features were often inadequate or inequitably distributed.
We simultaneously launched the Global Observatory of Healthy and Sustainable Cities to promote healthy and sustainable urban planning, benchmark and monitor cities’ progress, and share more consistent, comparable urban data. The whole series of articles is free and open access, as is our software.