I have a new article out now in The Journal of City Climate Policy and Economy, coauthored with a team that includes several of the folks from our recent series in The Lancet Global Health. The JCCPE article, “A Pathway to Prioritizing and Delivering Healthy and Sustainable Cities,” synthesizes findings and recommended policy actions arising from that recent TLGH series.
From the abstract:
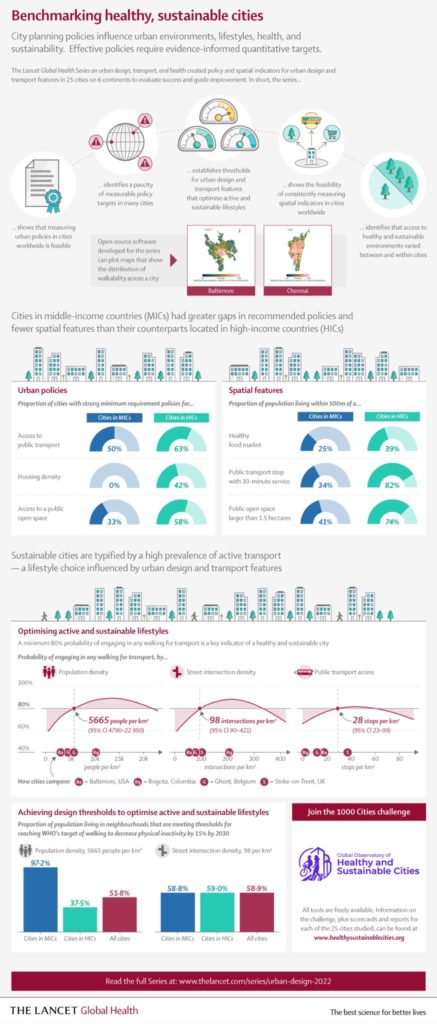
Creating healthy and sustainable cities should be a global priority. Some cities prioritize 15-minute cities as a planning approach with co-benefits for health, climate change mitigation, equity, and economic recovery from COVID-19. Yet, as our recent The Lancet Global Health series on “Urban Design, Transport, and Health” showed, many cities have a long way to go to achieve this vision. This policy guideline summarizes the main findings of the series, which assessed health and sustainability indicators for 25 cities in 19 countries. We then outline steps governments can take to strengthen policy frameworks and deliver more healthy, equitable, and sustainable built environments. The Lancet Global Health series provided clear evidence that cities need to transform urban governance to enable integrated planning for health and sustainability and commit to policy implementation. Evidence-informed indicators should be used to benchmark and monitor progress. Cities need policy frameworks that are comprehensive and consistent with evidence, with measurable policy targets to support implementation and accountability. The series provided evidence-informed thresholds for some key urban design and transport features, which can be embedded as policy targets. Policies and interventions must prioritize identifying and reducing inequities in access to health-supportive environments. Governments should also invest in open data and promote citizen-science programmes, to support indicator development and research for public benefit. We provide tools to replicate our indicators and an invitation to join our 1,000 Cities Challenge via the Global Observatory of Healthy and Sustainable Cities.
For more, check out the JCCPE article itself. And you may also be interested in our recent The Lancet Global Health series of articles that developed similar themes in great depth.