OSMnx version 2.0.0 has been released. This has been a massive effort over the past year to streamline the package’s API, re-think its internal organization, and optimize its code. Today OSMnx is faster, more memory efficient, and fully type-annotated for a better user experience.
If you haven’t used it before, OSMnx is a Python package to easily download, model, analyze, and visualize street networks and any other geospatial features from OpenStreetMap. You can download and model walking, driving, or biking networks with a single line of code then quickly analyze and visualize them. You can just as easily work with urban amenities/points of interest, building footprints, transit stops, elevation data, street orientations, speed/travel time, and routing.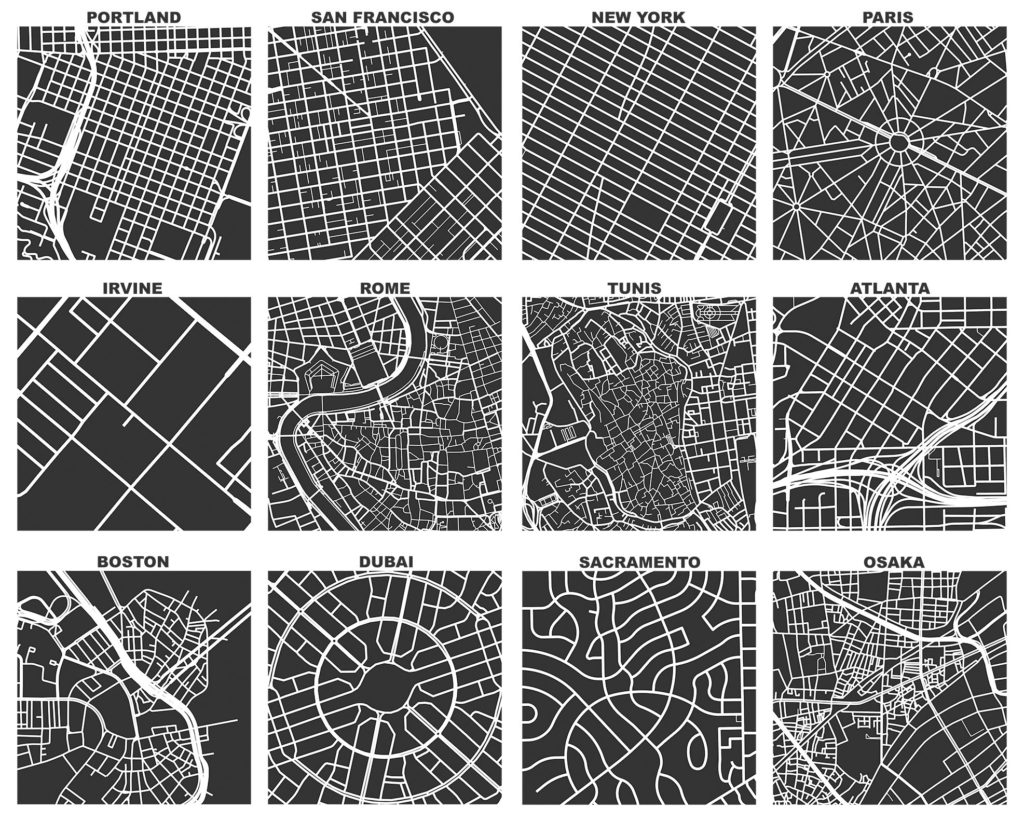 This has now been a labor of love for me for about 9 years. Wow. I initially developed this package to enable the empirical research for my dissertation. Since then, it has powered probably 2/3 of the articles I’ve published over the years. And it has received hundreds of contributions from many other code contributors. Thank you to everyone who helped make this possible.
This has now been a labor of love for me for about 9 years. Wow. I initially developed this package to enable the empirical research for my dissertation. Since then, it has powered probably 2/3 of the articles I’ve published over the years. And it has received hundreds of contributions from many other code contributors. Thank you to everyone who helped make this possible.
I hope you find the package as useful as I do. Now I’m looking forward to all of your bug reports.